 Daring men and their flying machines
Daring men and their flying machines
Story and photos by Jerry C. Smith
A stand-up comic once joked, “If God had meant for people to fly, He would have given them a lot more money.” He got pained laughs from several private pilots in his audience who knew what it costs to get a license, buy a plane, fly it, hangar it and keep it in safe condition.
Whether you’re rich or poor, the sky shamelessly seduces those who envy the freedom of birds. Prior to the late 1970s, aviation was well out of reach to most folks who did not fly for a living, but a few entrepreneurs found a way to bring powered flight to practically anyone with the courage to try it.
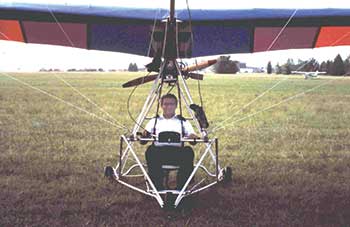
Imagine a huge kite made of ripstop Dacron sailcloth, a frame and pilot seat resembling an elaborate lawn chair, a couple of lawn-mower wheels and a tiny engine scrounged from a snowmobile. Lace it all together with a maze of steel cables and, voila, you have an ultralight airplane – a true bird of ‘pray.’
Ultralights quickly became a poor man’s magic flying carpet, a dream come true for those without the means or desire to own a “regular” airplane. If you could afford a decent fishing boat and were fairly adept with hand tools, you could build your own plane in a few dozen hours from a mail-order kit, then fly it from a nearby pasture.
Best of all, you didn’t need a license to fly one, and still don’t even to this day, as long as the plane meets certain federal guidelines of construction and operation. Flight training, if any, was given in two-seater variants by licensed local dealers, but many were flown entirely on guts alone.
Since a true ultralight has only one seat, that first test flight was also the pilot’s first solo in that type of plane, which can intimidate even a trained private pilot.
Odenville resident Hoke Graham was one of the first to fly and sell such machines in the area. He tells of trying to foot-launch his Easy Riser, one of the first ultralights, which originally had no wheels. It was actually an Icarus biplane hang glider which had been fitted with a tiny, 10 horsepower, two-cycle motor made by Chrysler.
Hoke relates, “When we test-ran the engine in my motorcycle shop, the propeller blast blew papers all over the place and slung oil everywhere before we could get it shut off. We like to have never got it all cleaned up.”
Ultralights became so popular so fast that the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) created a whole new category for them, outlined in Part 103 of Federal Aviation Regulations. In essence, ultralights were designed for a single pilot, flown locally for daytime recreational use only, and according to some stringent rules.
The plane could weigh no more than 254 pounds empty, carry a maximum of 5 gallons of fuel, and fly no faster than 55 knots at full power. It is illegal to fly an ultralight over an assemblage of people or settled area, after dark, or within controlled airspace where the big boys fly.
Because of weight and performance restrictions, ultralights have few if any spare parts. They’re shy on horsepower, creature comforts and redundant safety features found on more conventional aircraft.
It’s as minimalist as powered flight can possibly be, but for many, including your writer, they were the fulfillment of a boyhood dream. The Wright brothers would have loved them; indeed, their first Flyer would have qualified had it been made of lighter materials.
While there are still a few single-seaters around, sport aviation has shifted in more recent years to a two-seated variety, many of which look and handle almost identically to the standard version but aren’t true ultralights. You need a private pilot or light sport pilot license to fly one.
Besides all the various quasi-ultralight designs, the relatively-new light sport category includes home-builts, most experimentals and other small aircraft, such as Taylorcraft, Piper Cub and Breezy, which fall within a fully-loaded weight limit of 1,320 pounds.
Many two-seated derivatives use engines of as much as 100 hp, more than triple the power of older single-seaters, and can easily fly 90 mph. Because of a higher weight allowance, they can be outfitted with all kinds of instruments, safety equipment, redundant controls, etc that a Part 103 machine could never carry.
 Pell City’s Joe West owns such a plane. It’s a larger version of a Challenger ultralight, made in Moline, Ill., by Quad City Aircraft Ultralight Aircraft Corp. It has a much more powerful engine, two seats, larger fuel tank and is about double the weight of its ultralight sisters.
Pell City’s Joe West owns such a plane. It’s a larger version of a Challenger ultralight, made in Moline, Ill., by Quad City Aircraft Ultralight Aircraft Corp. It has a much more powerful engine, two seats, larger fuel tank and is about double the weight of its ultralight sisters.
Joe spent more than two years building it and holds one of the first light sport licenses issued in the area. His superbly crafted plane sports a dazzling green and white paint job and mounts a 52-hp engine designed especially for light aircraft by an Austrian firm, Rotax, which also builds snow machine engines for Bombardier of Canada. It allows him to cruise smoothly at 60 to 70 mph.
Joe is a real craftsman who is not averse to improvisation. In fact, the sheet metal for his instrument panel was salvaged from an old octagonal city stop sign. Everything on his plane is neat, precise and by-the-book, including an emergency parachute that can be instantly activated from both seats.
The plane’s nose art reads TINKER TOY, a moniker inspired by a fellow firefighter in Birmingham who liked to tease him about all the small airplane parts he fiddled with while not on duty, saying the intricate components looked like Tinker Toys.
He’s a frequent flyer around Pell City and has flown his Challenger for about 15 years. But Joe doesn’t limit his range of operations to local “patch-flying.” He and several other Challenger owners once flew from Pell City to a sponsored aviation meet in the Great Lakes region, near the Quad City factory.
Another local light-flyer, Cropwell contractor Tommy Thompson, is also a highly skilled artisan, both on the job and as an experimental aircraft hobbyist. He has built and flown four kit planes over the years, each a finely crafted work of flying art.
His Loehle P5151 Mustang was a 3/4 scale replica of one of the world’s finest warplanes. Tommy painted it blue, white and orange; named it Miss War Eagle; and was granted a tail number ending in WE. It was always a hit at air shows and fly-in events held by the Experimental Aircraft Association, of which Tommy was president of local Chapter 1320 until its dissolution in recent years.
So what’s it like to fly an ultralight or experimental? Depends on the design. Back in the 1980’s, your writer owned an American Aerolights Eagle. It had a smaller wing, called a canard, mounted in front of the main airfoil. This made it nearly stall proof and very easy to fly, even for a novice pilot. The Eagle took off, flew, climbed, descended and landed at about the same speed, 25-30 mph. We joked that, like a Piper Cub, it flew just fast enough to kill you.
I flew mine while suspended in a child’s swing seat which hung by a slender strap from a main body tube. Below this seat was nothing but open sky, all the way to the ground. Needless to say, that strap was rigorously inspected before every flight, as were all other vital parts which, in reality, included EVERY part of the plane.
Other models look and handle more like conventional aircraft, with true three-axis controls and the familiar T-shaped fuselage. Most ultralight aircraft can virtually leap off a runway in 200 feet or less and land in almost any clearing. Indeed, on occasion, these pilots would take off across the old bomber runway at Talladega.
But there is a penalty for this feather-like agility. You should not fly unless the air is mostly calm. Flights are usually made in early morning or near sunset. Planes stayed in the hangar if treetops were spotted moving.
I’ve encountered sudden gusts in advance of unseen weather fronts that actually left me flying backwards, despite running full throttle. My only recourse was to drop behind a treeline at almost ground level and quickly land before the wind shifted.
An unwritten rule was observed by practically everyone: Never fly over anything you can’t land on. With no redundant parts and an engine that could fail at any time without notice, keeping a landing spot underneath was mandatory.
But all such hazards aside, the flight itself was exhilarating, possibly the most fun a dauntless bird-man could have in public. We usually flew lower than 500 feet, enjoying the sights, even the smells, as rural Alabama drifted leisurely beneath our dangling rumps.
Our flying grounds included the environs of Talladega Speedway in our earlier days and Washington Valley and Chandler Mountain after we moved to Cool Springs near Ashville. It’s one of the most scenic parts of St. Clair — even more so from the air.
The good people of Cool Springs and Caldwell gracefully tolerated our weekend noise, so we always invited them to our airfield cookouts and watermelon cuttings. Livestock in Washington Valley became so accustomed to our presence that they no longer stampeded or looked up in fear of a giant, raucous hawk passing overhead.
The group I flew with in the early 1980s was known as Four Seasons Aviation, a three-man corporation operated by Hoke Graham, Jack Porter and Mike Pair. They sold Eagle ultralights and provided flight training, first at Talladega Airport, later at the Cool Springs site.
Cool Springs Airdrome was laid out on an old horse farm on CR 31, between Ashville and Springville, near Canoe Creek at AL 23. A former stable was modified to serve as a hangar and business office. The airstrip was simply 1,500 feet of closely-mown pasture.
Because of the Eagle’s unique configuration, we were able to store all five resident planes in a hangar that would have barely contained one “regular” plane. We simply tilted them upright and stood them on their tail feathers.
Four Seasons was a beehive of activity on nice weekends, often hosting fly-in visitors and curious kibitzers. Because of the capricious nature of these aircraft, we had a map mounted on a steel panel, with little colored magnets for each pilot to indicate where he intended to fly. We often flew in pairs, for the same reason.
On one such junket, a friend and I were flying over Washington Valley when he spotted some lovely young women lounging beside their swimming pool. He landed in a nearby field, but I decided it was no place for a married man and flew back to the airport.
Apparently he had chosen wisely, as we didn’t see him again until a bit after sunset. In a scenario reminiscent of an old flying movie, we lit the runway with car headlights to allow our resident Romeo to land safely.
A couple of areas were off-limits. One of our flyers was a deputy sheriff who warned us to avoid flying anywhere near the new St. Clair Correctional Facility as well as a certain area called Sodom and Gomorrah because of various activities that the law preferred to contain in that one place rather than having to pursue them all over the county.
Were there accidents among our ultralight community? Yes, even a few fatalities. But like real flyers everywhere, we studied and discussed each case, resolving to never become an object lesson ourselves.
For many, the incident rate became too high for comfort, so they moved on to earn a private pilot license and bought “real” airplanes. No doubt some wives added input to these decisions. However, many have since admitted that they became much better pilots as a result of things they’d learned from light flight.
Joe and I recently flew his Challenger on a photo shoot around the Pell City locality. We flitted along at a leisurely 65 mph, snapping photos of Logan Martin, downtown Pell City and certain areas north of town.
While a pure ultralight must not fly over settled areas, a rated experimental like Joe’s can be operated under more lenient standards. The visibility is spectacular to say the least, making them an ideal photo platform equaled only by glass-pod styled helicopters, and they’re exponentially cheaper to own and operate.
Another endearing quality is its real feel for flight, like you are actually involved in a natural process rather than riding an armchair in a giant flying bus. You sense every rising thermal, every wind shift and “air bump,” and enjoy a fast-acting, sensitive control response that makes you feel like part of the plane itself – a true mechanical bird-man connection. There’s no autopilot. You fly them every second from takeoff through landing.
Joe quipped that his plane is so well-balanced and control-sensitive that he can actually make it turn by sticking his hand out one side, like giving a turn signal. To a true light flight enthusiast, a 20-minute ride is often more satisfying, and physically tiring, than a couple of hours in a “real” airplane.
Born in Haleyville and a long-time resident of Birmingham, Joe once advised folks to never allow a hobby to dictate where you live, but reneged on his own tenet while flying and hangaring his craft at Pell City Airport.
“After hanging out around the airport, I found out what a nice place Pell City was, and decided to live here,” he said. Indeed, his home is within easy walking distance of the main entrance at KPLR.
At age 67, Joe has seen a lot of light aircraft makers come and go. Dozens of companies jumped into the market when the category was first created, but most are long since expired, usually with good reason.
Those early years were fraught with accidents, mostly due to design faults and pilot error. He advises those interested in light sport aviation to research FAA files and thoroughly check out the accident records of any aircraft they plan to purchase or build from a kit.
“Look for companies like Quad City that have been in business the longest, preferably under original ownership,” he says. He also advises to seek skilled, licensed training before attempting any solo flight in any aircraft, whether ultralight or otherwise. Even though they fly relatively slowly, irreversible things can happen very quickly.
He remarked that the handling characteristics of his Challenger makes him feel connected to early pioneers such as the Wright brothers. Having flown several such machines myself, I heartily agree. It’s the real thing – a natural high.
Though he’s a quiet, unassuming man to casual acquaintances, Joe’s sincere enthusiasm for this genre of aviation becomes obvious once you get to know him, fly with him, and check out the workmanship and safety record of his plane. Retired from the Birmingham Fire Department, he now works part-time at a local hardware big-box to, in his words, “make some flying and eating-out money.”
Joe says, “Sport aviation is sort of winding down as a hobby because the ones who started it are getting old, and nobody is replacing them. We need for more kids to get involved with groups like Civil Air Patrol and the EAA.”
He adds a sentimental note: “If someone ever gets a chance to go flying, especially someone who has never gone up, I strongly urge them to go up and see the sights that are restricted to a fortunate few people and to be mesmerized by the wonders that they have missed all their life.”
The late Glenn Messer, world’s oldest living pilot, who passed away just days short of his 100th birthday in 1995, expressed to me that one of his biggest regrets was that he never flew an ultralight. He had been blinded by a failed eye surgery a few years before these aircraft became popular.
Mr. Messer used to sit in the lobby at Birmingham’s Southern Museum of Flight and chat with visitors about his long, colorful flying career, which included giving Charles Lindberg a check ride in his new Curtiss Jenny back in the 1920s.
He should know of what he spoke. The pilot license he proudly showed to visitors was signed by Orville Wright.














