Finding where the bones are buried
Story by Elaine Hobson Miller
Photos by Wallace Bromberg Jr.
About 50 people gathered inside Reeves Grove Baptist Church on a fall Saturday, listening attentively as The Backwood Boys sang Ain’t No Grave (Gonna Hold This Body Down), Swing Low, Sweet Chariot and other old spirituals.
They heard a brief history of the church and received apples from the apron pockets of several women dressed in the fashion of the late 1800s, when the church was established.
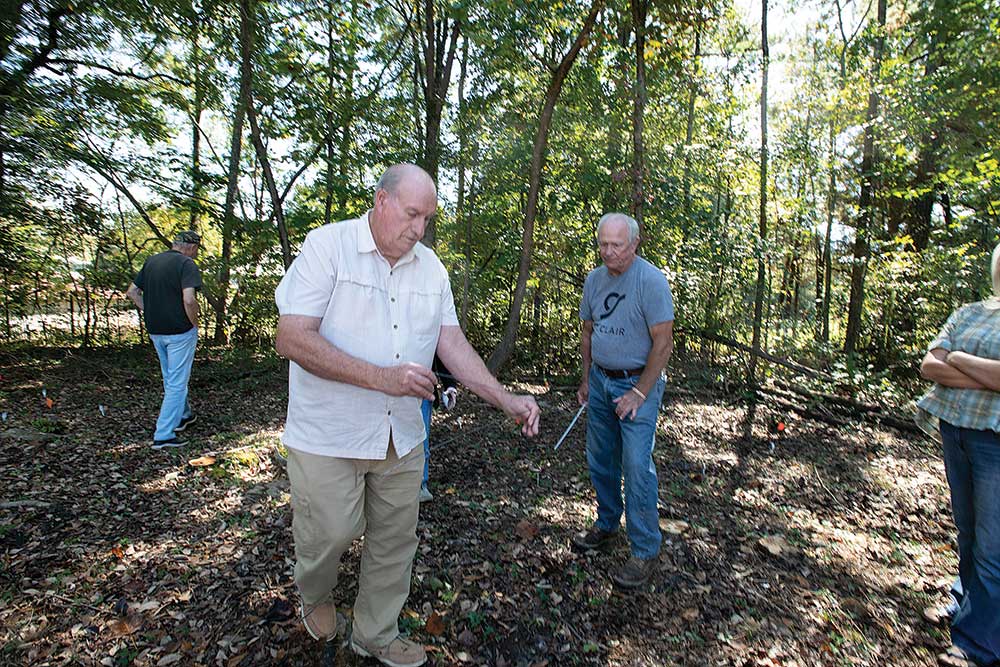
But the main attraction was outside, after these presentations, when two grave dowsers approached the old church cemetery, dowsing rods made of wire in their hands. Dowsing has been used for centuries to locate water, graves, pipelines and other underground objects by watching the motion of a pointer – usually a forked stick or paired bent wire. At Reeves Grove, the group was locating graves as part of its ongoing restoration project at the historic church.
It didn’t take long for Wayne Gregg’s rods to cross, indicating a grave. According to the marker, that grave belonged to Elizabeth McCorkle, wife of the original owner of the McCorkle Plantation upon which Reeves Grove now stands. Something wasn’t quite right, though. The markers weren’t where they were supposed to be. His rods indicated the presence of a second body that wasn’t represented on the grave marker. “We think it might have been Elizabeth’s husband,” says Linda Moyer, chairperson of the Reeves Grove Historical Committee.
The group soon moved on to the slave section of the cemetery, where the graves have no stones. The committee wants to mark those graves and give the folks buried there the recognition they are due, even if their names are unknown.
Gregg, who is from DeKalb County, wasn’t the first dowser to notice the anomaly of an extra person in a grave, however. “I went up there one afternoon with some members a week before they had the official event,” says Frank Waid, a Springville grave dowser who studied under Gregg. “We laid out the McCorkle Cemetery and marked a bunch of graves with flags. (Moyer says they put ribbons on the graves of the church founders.) One kept giving all kinds of problems. I was getting readings of male and female bodies. I said, ‘Something’s wrong here. I think there’s two people in this grave, but I’m not sure, because I’m not as experienced as Wayne Gregg.’ So, when they had the special day and demonstrated dowsing for the people, Wayne started walking in the spot where I had been walking and said, ‘There are two people buried here!’”
The dowsing event was another effort to raise awareness and money for the restoration of the original church building. The church historical committee is restoring the sanctuary and its attached fellowship hall to be used as an event venue.
But restoration wasn’t uppermost in the minds of those in attendance on dowsing day. People were so interested in Gregg’s presentation on grave dowsing that their questions and his answers pushed his allotted 30-45 minutes on the program to an hour. “They were fascinated,” says Moyer. “They also enjoyed Macki Branham’s brief history of the church and Glenda Tucker showing off a fashionable dress from the McCorkle era.” The dress was once worn by Eliza Elizabeth (Moore) Keith, (December 16, 1827-January 8, 1891), the great-great-grandmother of Glenda’s husband, Harry Tucker.
The Backwood Boys – Gallant musicians Adron and Mark Willingham on guitars, Marlin Galloway on mandolin – continued to play as the audience filed outside behind Gregg and Waid for the actual grave dowsing. Gregg narrated while Waid demonstrated dowsing techniques.
“I use two wires I got from Wayne,” Waid says. “If they cross high, it’s a female; if low, it’s a male. Lots of times (during the 1800s) women died in childbirth and they buried mom with her baby on her chest. Wayne can tell that, but I don’t have that experience yet.”
Waid noticed that all the graves in the slave section were small and wondered whether they might be buried in a fetal position. “They wouldn’t have had the resources for caskets, so they probably wrapped the bodies in blankets,” he said. “Most of these slaves came from South Carolina, and they were Caribbean slaves, so some of their beliefs determined how they were buried.”
Waid took a grave-dowsing class from Gregg about three years ago at his wife’s urging. She is a member of area historical and genealogical societies and thought grave dowsing might add depth (no pun intended) to that type of research.
“He gave a long, interesting class that morning, we had lunch, then went to an old cemetery,” Waid says. “We started practicing dowsing. Somehow it seemed to work for myself and Joseph Williams, also from Springville and part of the Springville Preservation Society. It was amazing! There were some people there who couldn’t get the hang of it, or it didn’t work for them, but for Joseph and me and one other lady, it did.”
In a self-published booklet titled, Dowsing for Fun and Profit, Gregg writes, “In Peru, a rock carving more than 9,000 years old depicts a man holding a forked dowsing stick,” he writes. Modern dowsing begins to appear in records around the 15th century in Europe.
Although most scientists are skeptics, Gregg says dowsing has been proven many times. “I recently read a German government 10-year report recorded by a physicist at the University of Munich,” he says in his booklet, which he published several years ago. “He described how dowsing was used to locate water sources in arid regions of Sri Lanka, Zaire, Kenya, Namibia, Yemen and other countries. The success rates by dowsers in 691 drillings was an amazing 96%, where a success rate of only 30% would be expected from conventional techniques.”
Gregg got interested in dowsing when he went to work for Southern Bell telephone company in 1963. “The older guys who repaired underground cables taught me,” he says. “We didn’t have the modern devices we have now.”
Although dowsing is sometimes related to spirituality and witchcraft, Gregg says he doesn’t have any special powers, nor is he gifted in any way. It has nothing to do with witchcraft, because “it works for the majority of those who try it, and I know we are not all witches.” At times he has thought he discovered what makes it work, such as disturbance of the earth’s energy fields, only to find it was not true, particularly when it comes to determining the gender of a person in a grave. “Albert Einstein referred to dowsing as quantum physics, yet unexplained,” he says.
Still, people for whom the stick worked were called “water witches” by our ancestors, who hired them to locate underground water. “Rods work for a large percentage of first timers,” Gregg says. “Forked sticks work for only a very small percentage.”
For grave dowsing, he uses wire rods, which can be made of any stiff wire. The most common are coat hangers. The rods are made by bending the wire into an “L” shape, with the handle being the length of the dowser’s hand and the long part extending in front of him for 12-18 inches. “Rods will work for a large percentage of those who try for the first time,” he writes in his booklet. “They will never work for some, no matter how hard they try. Excessive jewelry, cellphones and other items worn on the body will sometimes make a difference.”
In his booklet, he explains how to hold the rods (elbows at waist, forearms parallel to the ground). He cautions NOT to place one’s thumbs over the bend of the handle, as this will restrict movement. Don’t grip too tightly, he cautions, only enough to keep the rods parallel. Approach the gravesite walking very slowly. “The rods will cross in front of you when you are over the grave. Once you step off the grave, they will uncross.”
He says the rods will respond the same to any burial, including stillborn infants through adults, even animals. “It makes no difference if the body was buried wrapped only in cloth, in a wood or metal coffin, or a coffin inside a vault,” he writes. “The age of the grave makes no difference. It can be recent or hundreds of years old.”
He says in order to more easily find unmarked graves and determine gender, it’s important to remember that most cemeteries in the United States bury their dead in a Christian manner. Their bodies are laid on their backs with their heads pointing west and their feet pointing east, as if they’re looking east for the second coming of Jesus Christ.
“You will discover that unmarked graves in an established cemetery will be buried in the same rows as marked graves,” he writes. “In a cemetery with no markers, it will be necessary to determine east and west directions to know the position of graves. Locate unmarked graves by walking slowly across the area you suspect. If graves are present your rods will cross and uncross as you move from one grave to the next.” Above all, he says, practice, practice, practice to get good at dowsing.
At 80 years of age, Gregg doesn’t dowse as much as he used to. He doesn’t have plans to conduct another workshop, either, but his booklet, which also discusses dowsing for water pipes and buried cables, is available, along with two wire dowsing rods, for $10.
Several folks at the Reeves Grove dowsing event bought the package, and just about everyone came away with a new perspective on the subject.
“Through the years, the McCorkle property gradually got sold bit by bit to various people, and we found out the day of the dowsing event that the original cemetery probably extends into what is now the Fant property,” Moyer said. “Now we know where the graves actually are in the old slave section.”
Editor’s note: For more about the restoration project, go to discoverstclair.com/back-issues and scroll down to April 2019, page 42.
Call Gregg at 256-706-3262 for information on how to obtain the booklet and rod set.
































